Managing local Admin Groups on Windows trough Microsoft Intune
06 February 2025
Managing Local Windows Groups through Intune Account Protection Policies
In an enterprise environment, managing local Windows groups such as Administrators
and Remote Desktop Users is critical for ensuring secure access to systems. Intune,
Microsoft’s mobile device management (MDM) platform, offers powerful Account Protection
policies that can help administrators enforce security settings for these groups.
By leveraging Intune’s capabilities, organizations can standardize access control,
minimize security risks, and ensure compliance across devices.
What are Account Protection Policies?
Account Protection policies in Microsoft Intune allow administrators to configure security
settings for user accounts, including those tied to local Windows groups. These policies are
particularly useful in managing who has elevated privileges and remote access permissions,
such as users in the Administrators or Remote Desktop Users groups.
Managing Local Groups with Intune
Here’s how Intune can help manage local Windows groups effectively. For this example we
will configure the local Administrators group to prevent privileged users to manipulate this group.
First we need to open the Intune portal
and navigate to the Endpoint protection blade, right into the Account protection view.
Here create a new policy:
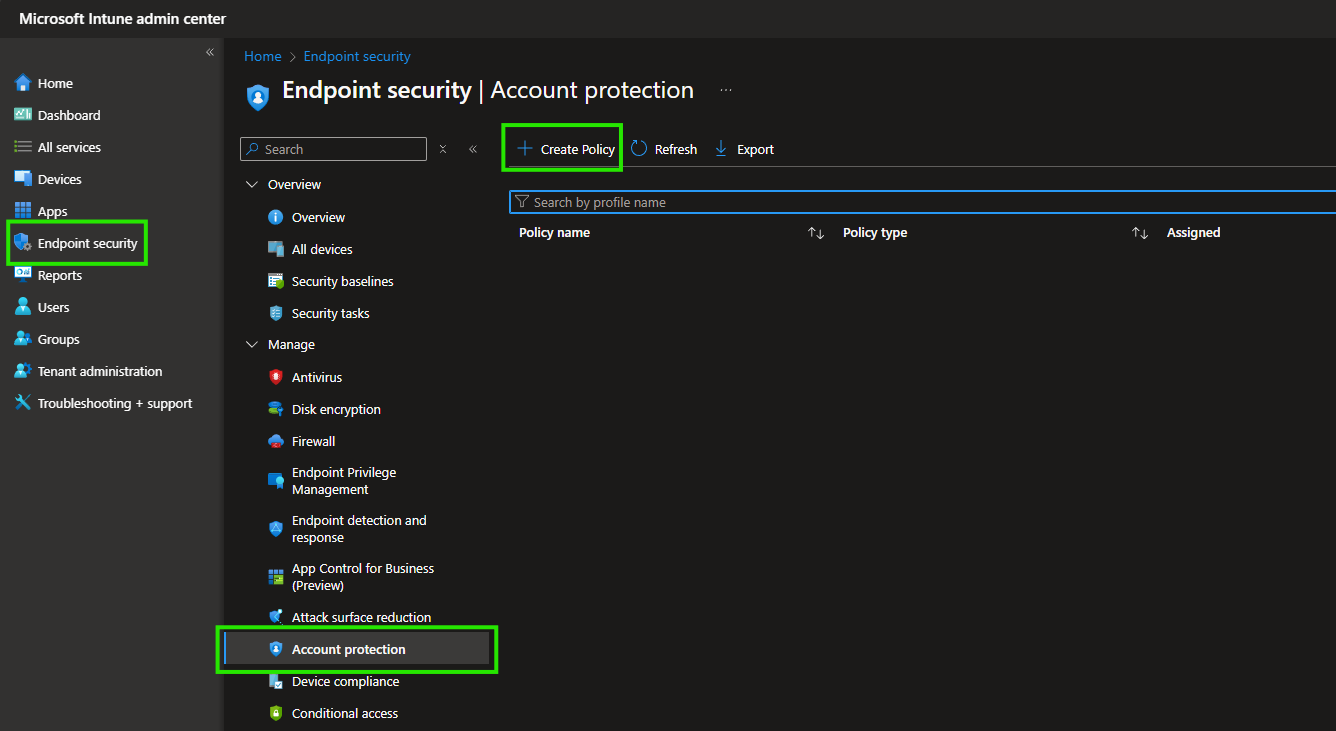
The policy needs to be from the Local user group membership type:
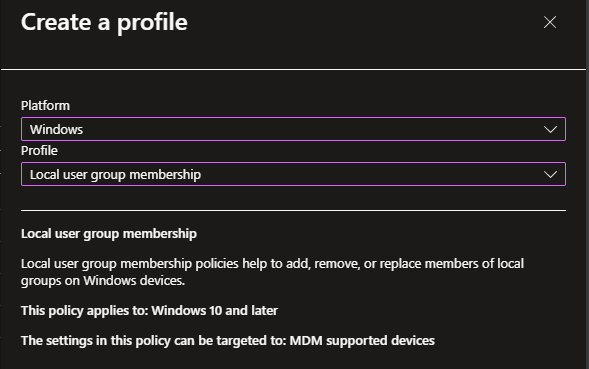
Define a Name and Description as you like:
Now click on + Add and choose one of the well-known local groups from Windows.
Here we will configure the Administrators group. If you want you can check multiple groups but for a simpler
management I would recommend to split them up.
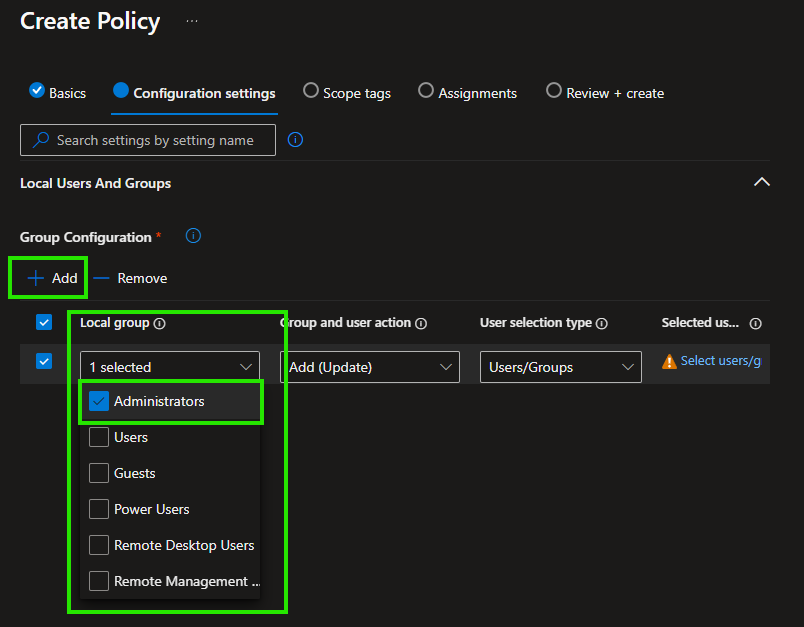
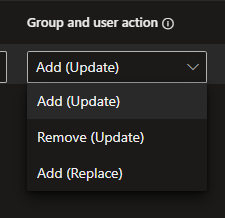
You can choose between
Add (Update)- this option simply adds users to the group.
Remove (Update)- this option can be used to remove users from the group as they will not be removed if you delete them from an Add (Update) policy.
Add (Replace)- this is the most secure as it fixes the members and if somehow anyone is added, with the next sync the group will be back in the configured state from this policy.
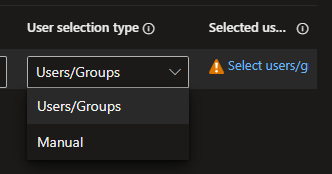
Now of course we need to define users. Here we habe the option to pick Users/Groups with a simple picker from Entra ID.
Or a Manual mode. I would preferr the Manual mode as this is the only option to also add the local Administrator account build-in to Windows.
If you want to use Windows Laps then you defenitely want to add this account and ensure that it is in the local Administrators group.
For this example we will choose Manual for the above described usecase.
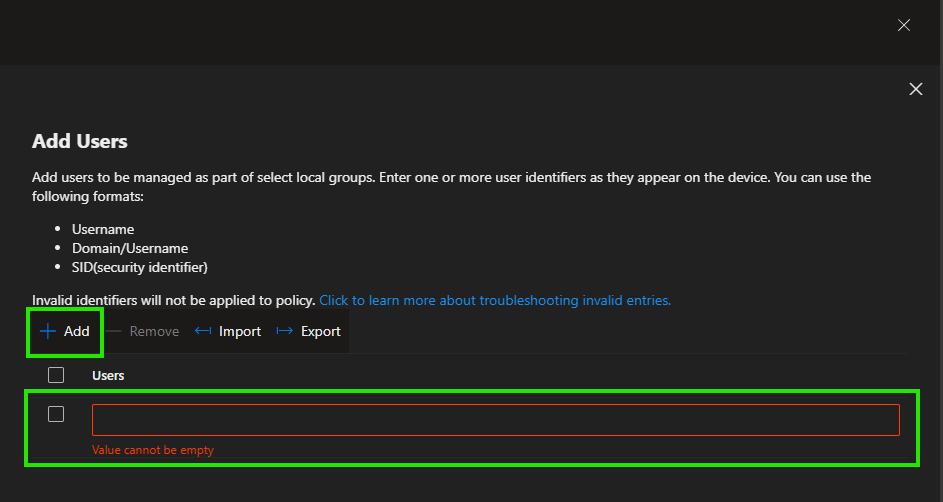
In Manual mode you can add [local] Usernames, [entraId or AD] Domain/Username and SID to a group policy.
There is a nice tool available HERE to convert Entra ID Object IDs
from groups to SIDs. Which you need to add Entra ID groups.
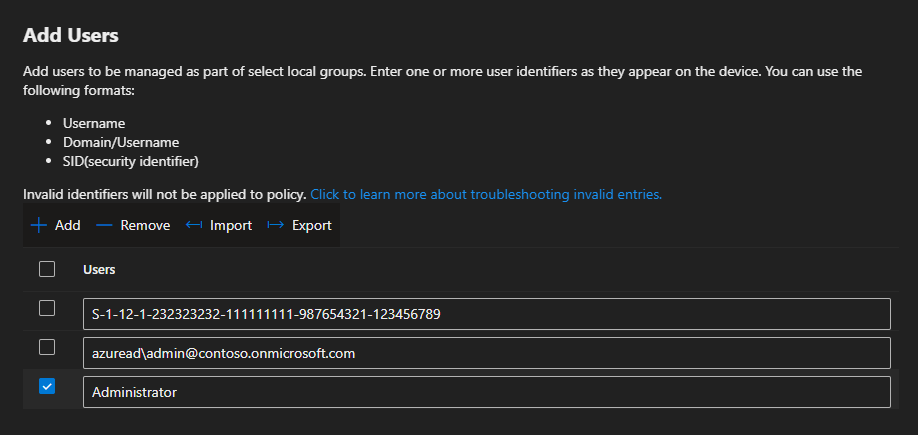
This example policy has the SID from an Entra ID group, followed by an Entra ID user and the local Administrator account.
Benefits
- Centralized Management: Admins can manage user access to critical groups directly through Intune, reducing the need for manual interventions on individual devices.
- Security and Compliance: Automating and enforcing these settings ensures that only authorized users have access to sensitive systems, helping organizations stay compliant with security standards.
- Efficient Remediation: Quick remediation and audit capabilities reduce the risk of errors and help maintain security hygiene across the organization.
Conclusion
Using Intune to manage local Windows groups like “Administrators” and “Remote Desktop Users” simplifies administrative overhead and strengthens security in an enterprise environment. By setting clear Account Protection policies, organizations can ensure that only authorized users have elevated privileges or remote access, reducing the risk of security breaches.