Attack Surface Reduction with Defender for Endpoint
31 December 2023
Attack Surface Reduction with Defender for Endpoint
What ist a Attack Surface?
Attack surfaces are any place where organizations are vulnerable to cyber threats and attacks. Defender for Endpoint includes numerous features that can be used to reduce the attack surfaces. All points at which companies are exposed to cyber threats and attacks are referred to as attack surfaces. Various features in Defender for Endpoint can help reduce attack surfaces.
The attack surface reduction rules that can be configured in Intune apply to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Plan 2, Microsoft 365 Defender, and Microsoft Defender Antivirus. There are some ASR rules that can be created using Microsoft Intune, we’ll go into that later in this post.
Microsoft recommends testing how Intune ASR rules affect the organization before enabling them by running the ASR rules in audit mode for a short period of time. While the rules are running in audit mode, any business-specific applications that may be incorrectly blocked can be identified and excluded from ASR. One should start with a small controlled group to limit potential work disruption and later expand deployment to the entire organization.
ASR Requirements
The Intune ASR policies are supported on the following operating systems:
- Windows 10 Pro, version 1709 or later
- Windows 10 Enterprise, version 1709 or later
- Windows Server, version 1803 (Semi-Annual Channel) or later
- Windows Server 2016, 2019 oder 2022
- Windows Server 2012 R2
In addition, the following features/licenses must be available:
- Microsoft Defender Antivirus (Real-Time Protection On)
- Cloud-Delivery Protection On
- Windows 10 Enterprise E3/E5
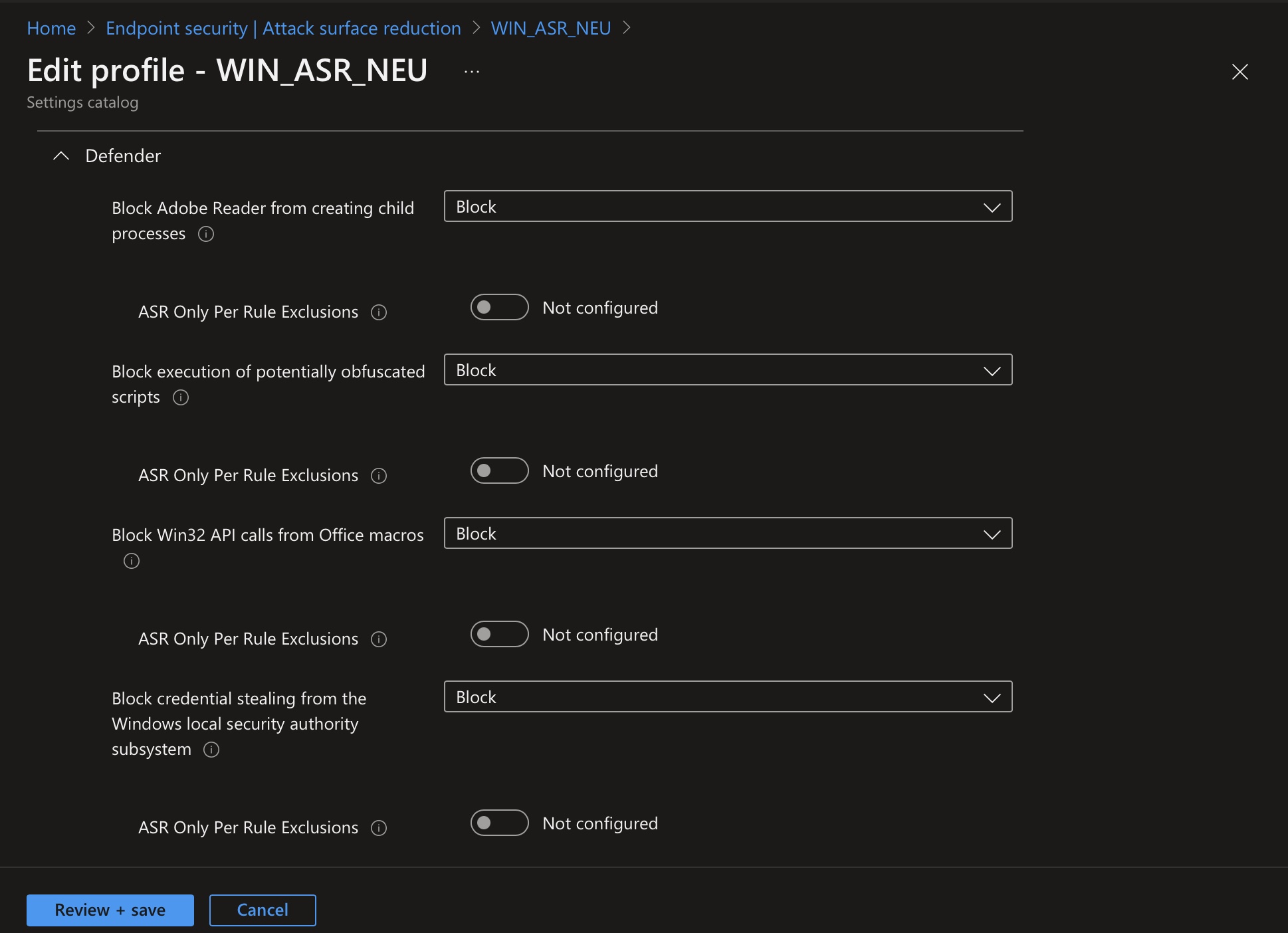
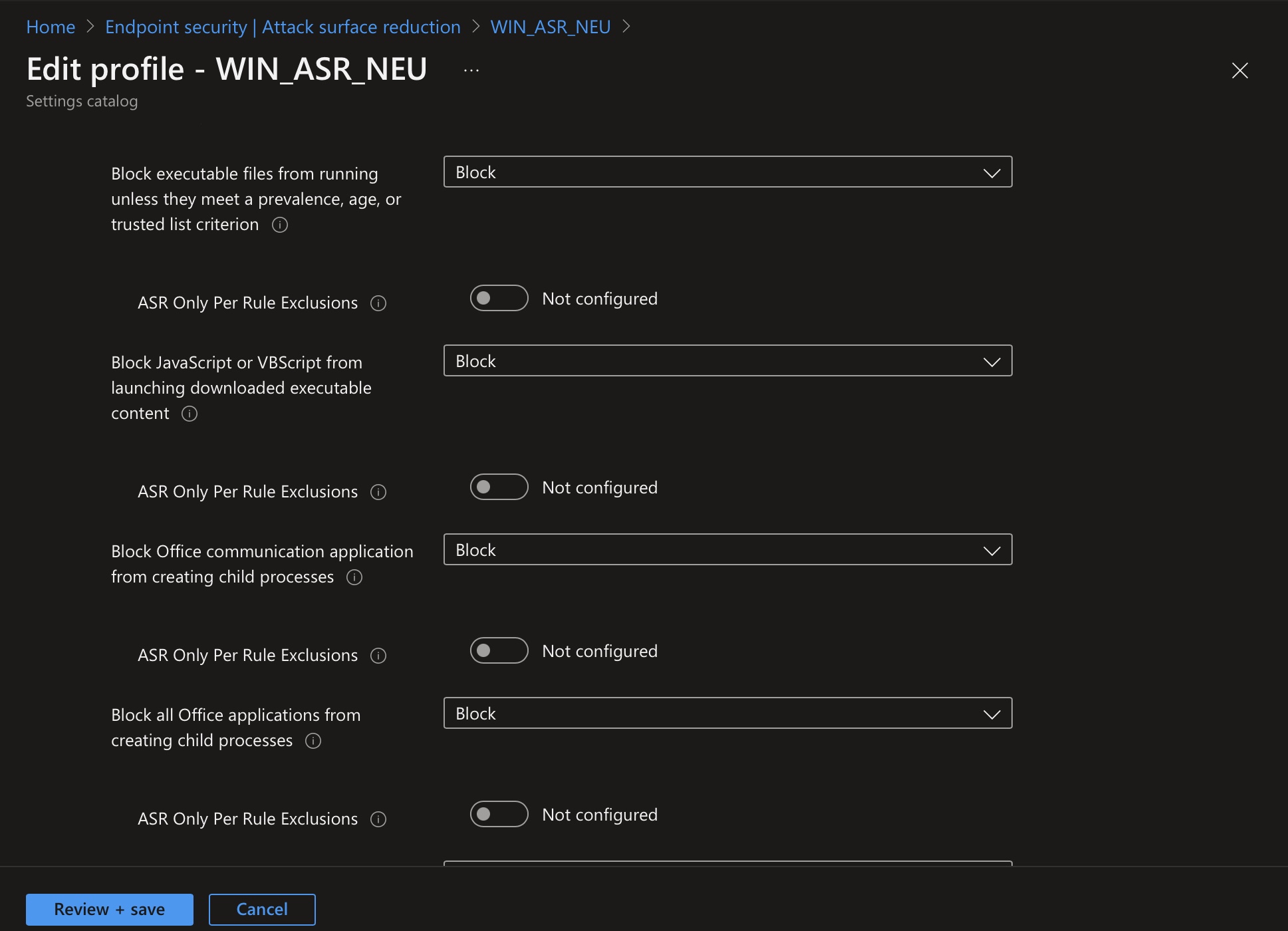
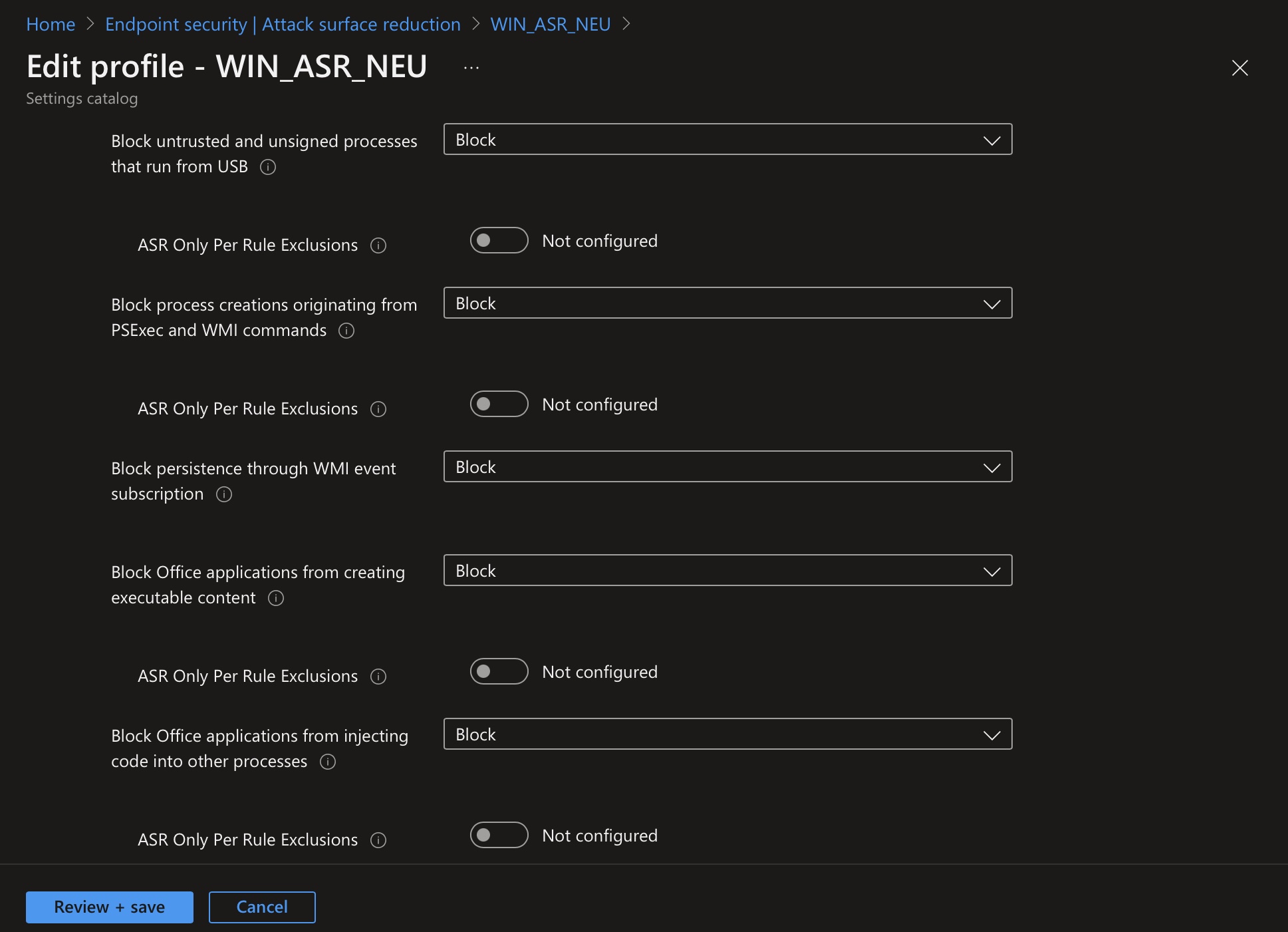
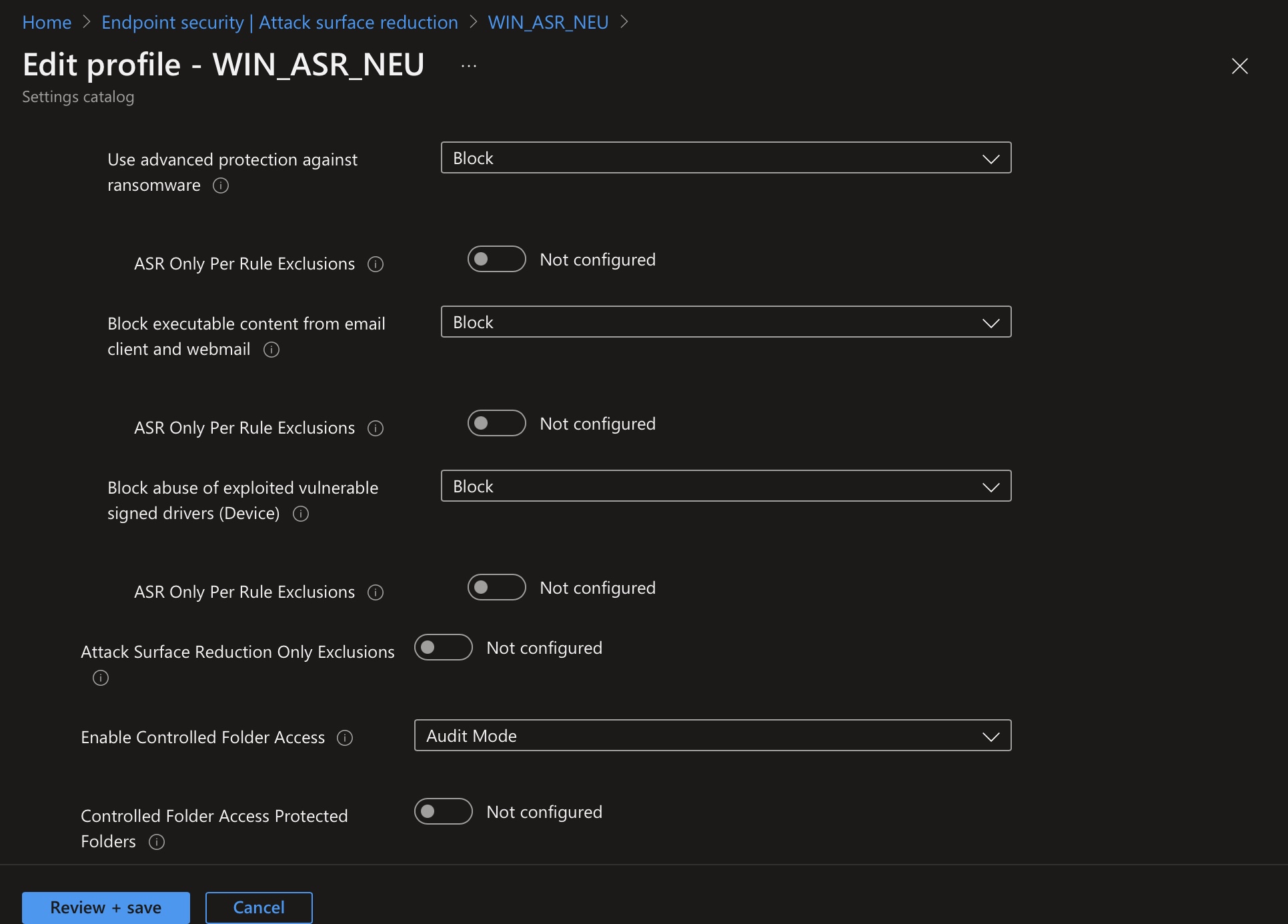
ASR Rules
| Rule Name | Description | GUID |
|---|---|---|
| Block abuse of exploited vulnerable signed drivers | This rule prevents an application from writing a vulnerable signed driver to the disk. Vulnerable signed drivers can be exploited by local applications – with sufficient permissions – to gain access to the kernel, potentially compromising the system. | 56a863a9-875e-4185-98a7-b882c64b5ce5 |
| Block Adobe Reader from creating child processes | This rule prevents attacks by blocking Adobe Reader from creating processes. | 7674ba52-37eb-4a4f-a9a1-f0f9a1619a2c |
| Block all Office applications from creating child processes | This rule prevents Office apps from creating child processes. Office apps include Word, Excel, PowerPoint, OneNote, and Access. | d4f940ab-401b-4efc-aadc-ad5f3c50688a |
| Block credential stealing from the Windows local security authority subsystem (lsass.exe) | This ASR rule prevents credential theft by blocking the Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS). LSASS authenticates users who log in to a Windows computer. Microsoft Defender Credential Guard in Windows normally prevents attempts to extract credentials from LSASS. | 9e6c4e1f-7d60-472f-ba1a-a39ef669e4b2 |
| Block executable content from email client and webmail | This rule prevents the following file types from being executed in emails opened in Microsoft Outlook or Outlook.com, and other popular webmail providers. | be9ba2d9-53ea-4cdc-84e5-9b1eeee46550 |
| Block executable files from running unless they meet a prevalence, age, or trusted list criterion | This ASR rule prevents executable files such as .exe, .dll, or .scr from running. Starting untrusted or unknown executable files can be risky as it is unclear whether the files are malicious. | 01443614-cd74-433a-b99e-2ecdc07bfc25 |
| Block execution of potentially obfuscated scripts | This rule detects suspicious characteristics in an obfuscated script. Malware authors and legitimate software developers often use script obfuscation to conceal intellectual property or speed up script loading. Malware developers also use obfuscation to make malicious code harder to understand and prevent it from being properly analyzed by security tools and humans. | 5beb7efe-fd9a-4556-801d-275e5ffc04cc |
| Block JavaScript or VBScript from launching downloaded executable content | This ASR rule prevents scripts from launching potentially harmful downloaded content. Malware written in JavaScript or VBScript often acts as a downloader to fetch and run other malware from the internet. | d3e037e1-3eb8-44c8-a917-57927947596d |
| Block Office applications from creating executable content | This rule prevents Office apps, including Word, Excel, and PowerPoint, from creating potentially harmful executable content by preventing malicious code from being written to disk. | 3b576869-a4ec-4529-8536-b80a7769e899 |
| Block Office applications from injecting code into other processes | This rule blocks attempts to inject code from Office apps into other processes. Attackers may try to use Office apps to migrate malicious code through code injection into other processes, allowing the code to disguise itself as a clean process. | 75668c1f-73b5-4cf0-bb93-3ecf5cb7cc84 |
| Block Office communication application from creating child processes | This rule prevents Outlook from creating child processes, while still allowing legitimate Outlook functions. | 26190899-1602-49e8-8b27-eb1d0a1ce869 |
| Block persistence through WMI event subscription | This rule prevents malware from abusing WMI to achieve persistence on a device. | e6db77e5-3df2-4cf1-b95a-636979351e5b |
| Block process creations originating from PSExec and WMI commands | This ASR rule blocks the execution of processes created via PsExec and WMI. Both PsExec and WMI can execute code remotely. Malware may abuse PsExec and WMI for command and control purposes or spread an infection across an organization’s network. | d1e49aac-8f56-4280-b9ba-993a6d77406c |
| Block untrusted and unsigned processes that run from USB | This rule allows administrators to block unsigned or untrusted executable files from running from USB drives, including SD cards. Blocked file types include executable files (such as .exe, .dll, or .scr). | b2b3f03d-6a65-4f7b-a9c7-1c7ef74a9ba4 |
| Block Win32 API calls from Office macros | This rule prevents VBA macros from calling Win32 APIs. | 92e97fa1-2edf-4476-bdd6-9dd0b4dddc7b |
| Use advanced protection against ransomware | This rule provides an additional layer of protection against ransomware. It uses both client and cloud heuristics to detect whether a file resembles ransomware. | c1db55ab-c21a-4637-bb3f-a12568109d35 |
ASR Hardening Policy
The following example shows an ASR policy that can be used to harden the client and closes many security gaps in advance: