Power up your software packaging with PSAppDeployToolkit
31 December 2023
How to use PSAppDeployToolkit?
In the world of software deployment, efficiency and accuracy are the keys to ensuring a smooth and seamless process. Fortunately, tools like PSAppDeployToolkit have emerged to simplify this process and offer a more streamlined approach to software packaging. This blog post aims to provide a comprehensive guide on how to utilize this tool, specifically for creating software packages for Microsoft Intune. So, whether you’re a seasoned IT professional or just getting started in the field, this post is sure to provide valuable insights.
Acquiring PSAppDeployToolkit
PSAppDeployToolkit, also known as PowerShell App Deployment Toolkit or short PSADT, is an open-source tool that IT professionals can use to simplify the process of creating and deploying software packages. It’s a powerful tool that provides a wide range of features, including interactive prompts, system restarts, and logging. To acquire this tool, you can visit the official GitHub repository
https://github.com/PSAppDeployToolkit/PSAppDeployToolkit
and download the latest stable release.
How PSAppDeployToolkit works
Creating software packages for Microsoft Intune using the PSAppDeployToolkit is a relatively straightforward process. First of all we need to download the Toolkit which is available on Github.
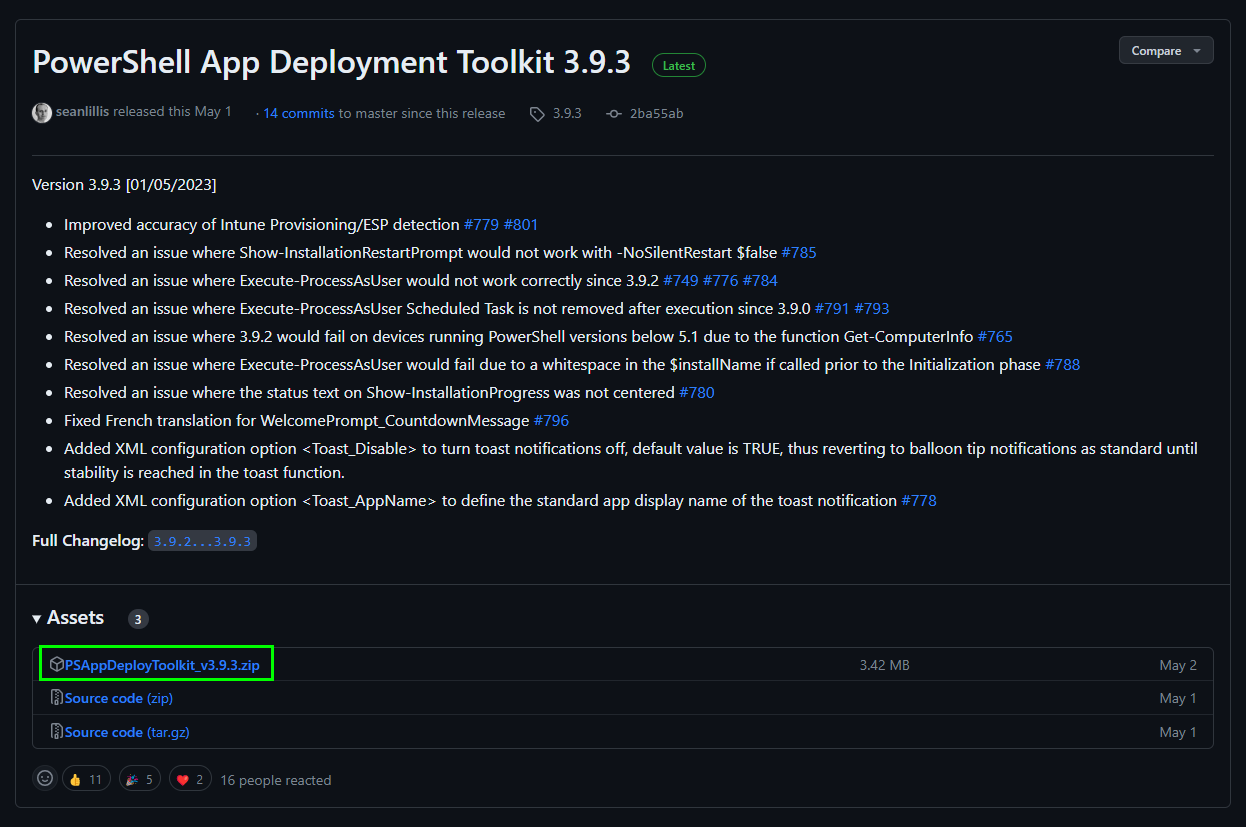
Next we need to extract the Toolkit folder
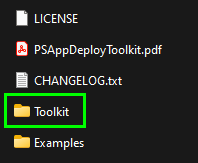
Inside the Tookit folder you will see the following files and folders:
Lets quickly talk about those files and folders and what they are for:
- Deploy-Application.ps1:
- In this script we have the logic for Installing, Uninstalling and Repairing an app. When you edit the script in PowerShell ISE or Visual Studio Code it helps when you run it once as you then have Autocomplete for the PSADT functions and Syntax fullfillment.
- Deploy-Application.exe.config:
- This config file tells the tool which version to use. You do not need to touch this file.
- Deploy-Application.exe:
- This tool uses the Deploy-Application.ps1 content to install, uninstall or repair your app and create the UI.
- AppDeployToolkit:
- Inside this folder you will find some scripts which are part of the Toolkit.
- SupportFiles:
- In the SupportFiles folder you can place configuration files or things that you need for the app installation except of the main installer file.
- Files:
- In the Files folder you should place the app installer which for example can be an .EXE or .MSI file.
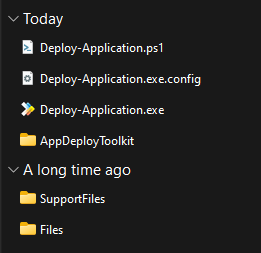
Now lets see what we have in the „AppDeployToolkit“ folder:

- AppDeployToolkitBanner.png
- This 450×75 px image will be the header of the tool. Modify it to add your corporate branding to the tool.
- AppDeployToolkitConfig.xml
- With this config file you can change the settings for the tool. For example the log path and how the log style is written.
- AppDeployToolkitExtensions.ps1
- This script allows you to extend the toolkit with custom functions.
- AppDeployToolkitHelp.ps1
- Run this script to open a UI which tells you everything about the available commands from the tool and how you need to call those.
- AppDeployToolkitLogo.ico
- This is the icon of the tool, modify it to add your corporate branding to the tool.
- AppDeployToolkitLogo.png
- This is the icon of the tool, modify it and convert it to .ico to add your corporate branding to the tool.
- AppDeployToolkitMain.cs
- This is the source code of the Deploy-Application.exe. Do not change it.
- AppDeployToolkitMain.ps1
- This script contains the PSADT core runtime and functions
Add installation sources to the „Files“ folder
Using PSAppDeployToolkit with Microsoft Intune
Lets have a look on how to add your routines to the Deploy-Application.ps1 script.
To add an Install routine you have a PRE-Install, Install and POST-Install phase.
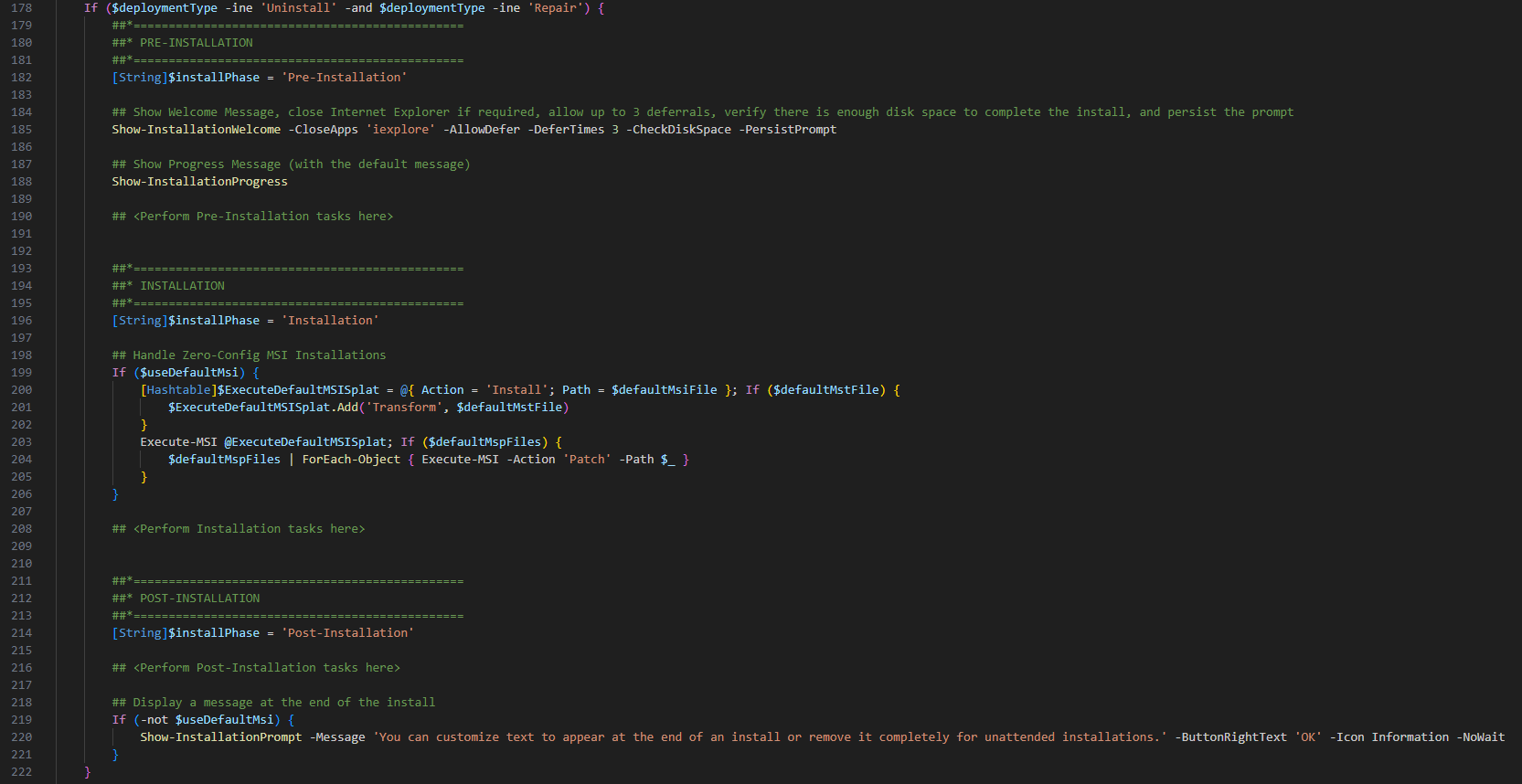
PRE-INSTALL
Here you can add pre-install task like for example to close apps which would disturb the installer.
INSTALL
Under line 208 add the logic to install your app. Here you can use build-in functions from PSADT to install .EXE or .MSI apps
MSI: Execute-MSI -Action 'Install' -Path 'setup.msi' -Parameters '/QN'
EXE: Execute-Process -Path "$Files\setup.exe" -Parameters '/S' -WindowStyle 'Hidden'
POST-INSTALL
This section is very helpful if you need to add configurations or registry keys after the installation to customize the app to your needs.
Next lets talk about the Uninstall section. Here you also have a PRE-Uninstallation, Uninstallation and POST-Uninstallation section which have the same options as in the Installation section but to remove the app from your endpoint.
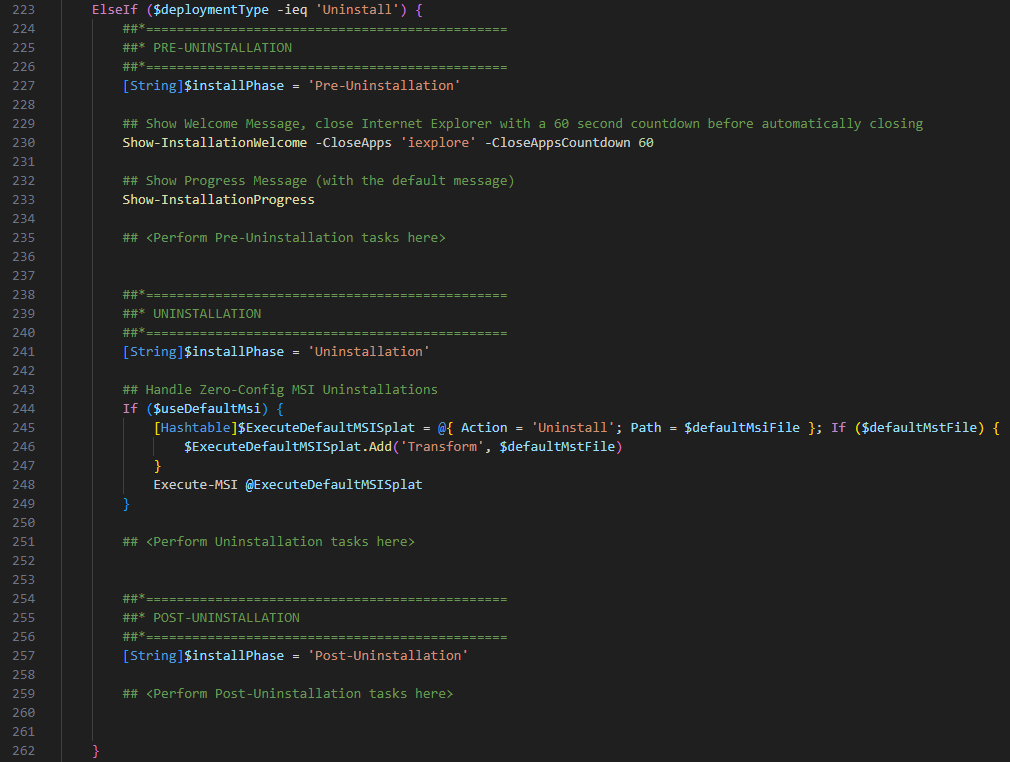
Next lets talk about the Repair section. Here you also have a PRE-Repair, Repair and POST-Repair section which have the same options as in the Installation and Uninstallation section but to repair the app from your endpoint.
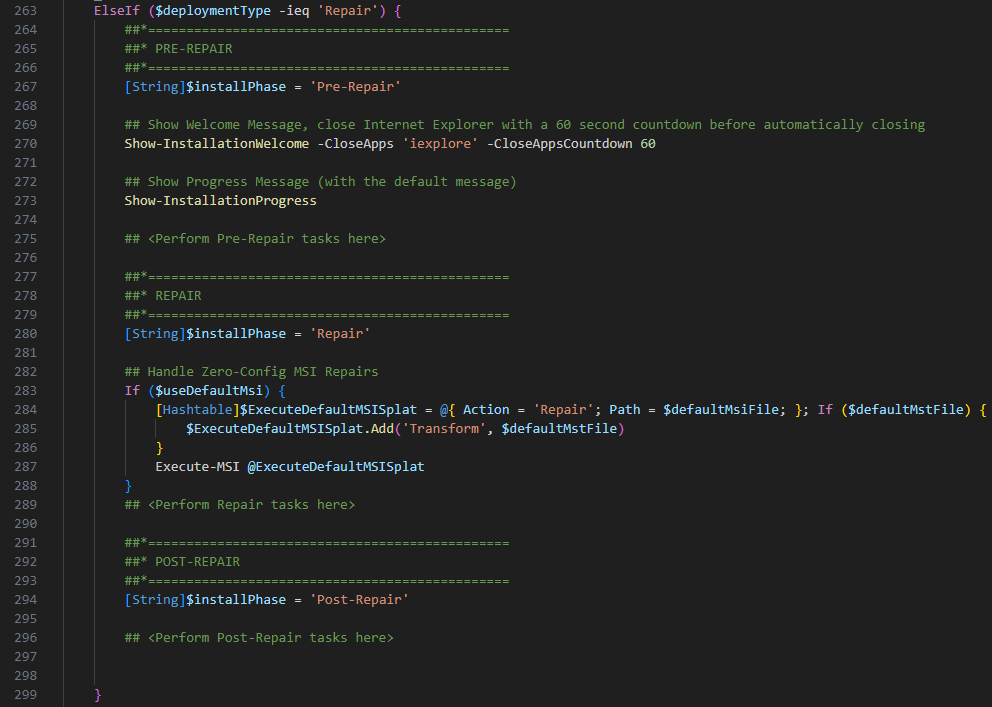
Once you have added the code for the Install, Uninstall and Repair sections, simply convert the contents to .INTUNEWIN – save and upload to Intune und assign the package to your devices:

Dean Ellerby created this video about the PSADT where he also tells how it works and how you can use it, check it out it is a very nice video:
Tips and Tricks
When using PowerShell ISE or VSCode run the AppDeployToolkitMain.ps1 script one time before you start to enable Autocomplete and Syntax correction.
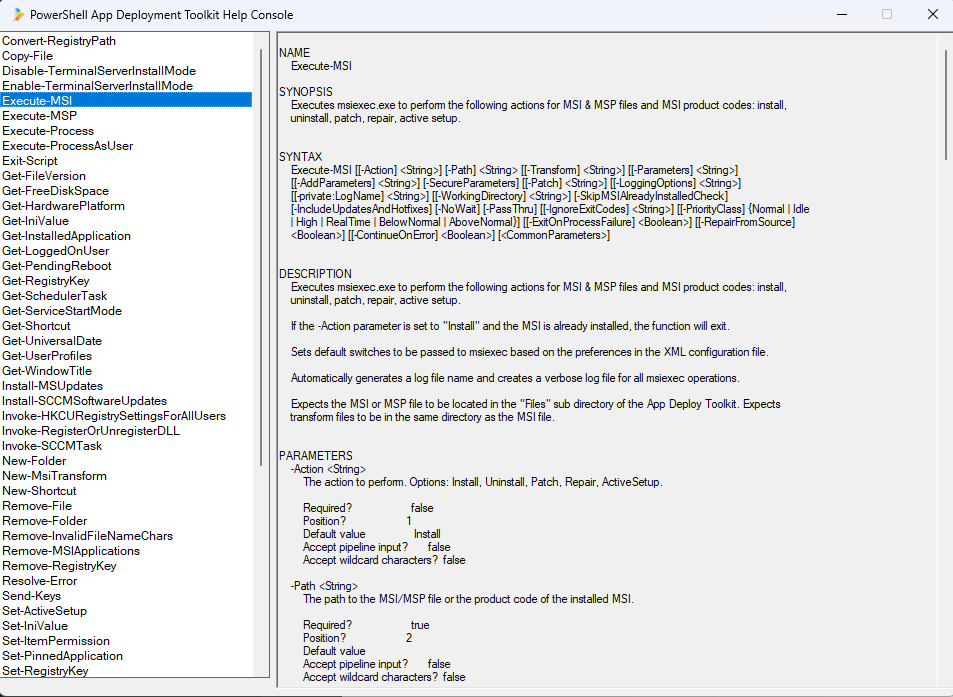
Use the AppDeployToolkitHelp.ps1 script to see all available commands with the parameters and how you need to use them:
Also check out my earlier post on how to use the Intune Management Extension Logs folder to save custom log files there and use the „Collect diagnostics“ from the Intune portal:
http://niklasrast.com/2023/09/25/quick-tip-optimize-troubleshooting-in-intune-by-saving-logs-in-the-intune-logs-folder/
Conclusion
The PSAppDeployToolkit is a robust and versatile tool that can significantly simplify the process of creating and deploying software packages, especially for Microsoft Intune. It provides several features that allow you to customize the installation process to suit your needs. However, like any tool, it requires practice to fully master. So, spend some time exploring the toolkit, and soon, you’ll be packaging software like a pro.