Windows Autopatch – An overview from my pov
31 December 2023
What is Windows Autopatch?
Windows Autopatch is a cloud service that can automatically deploy Windows, Microsoft 365 Apps, Microsoft Edge, and Microsoft Teams updates to improve security and productivity in organizations. This service can be configured and used through Microsoft Intune.
Benefits of Autopatch
Closing Security Gaps: By keeping software up to date, there are fewer security risks and device threats.
Closing Productivity Gaps: Delivering features as they become available gives users new tools to streamline workflows.
Streamline IT admin resources: By automating routine tasks like patching devices, IT admins have more time to implement optimizations.
Software-as-a-Service: By using SAAS, investments in local hardware can be minimized since updates are provided via the cloud.
Onboarding new services: Windows Autopatch is designed to be easy to deploy and minimize patching time.
Minimizing down times: Release in separate update rings optimizes reliability and compatibility for users. User interruptions due to updates are minimized.

Requirements
Licenses
Appropriate licensing is required to use the Windows Autopatch Service.
- Windows 10/11 Enterprise E3
- Windows 10/11 Enterprise E5
- Microsoft 365 E3
- Microsoft 365 E5
Network
To use autopatch, clients must reach the following Microsoft network endpoints: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/deployment/windows-autopatch/prepare/windows-autopatch-configure-network
Operating Systems
Windows Autopatch supports the operating systems Windows 10/11 Pro, Windows 10/11 Enterprise, and Windows 10/11 Pro for Workstations in the 64-bit version.
The clients must all be registered in Corporate-Owned-Personal-Enabled (COPE) mode, Bring-Your-Own-Device (BYOD) is currently not supported!
Clientmanagement Systems
The cloud service can only be used via Microsoft Intune or Microsoft Configuration Manager.
Usermanagement
Identities in Azure AD are required for the configuration. Because of this, the user accounts used must be Azure AD or Hybrid Azure AD objects. To be able to activate Windows Autopatch in a tenant, a user with the Azure AD role „Global Administrator“ is required.
Setup in Microsoft Intune
In this post, we will configure the service to work with Microsoft Intune. Configuration is possible in the Endpoint Manager under „Tenant Administration“:
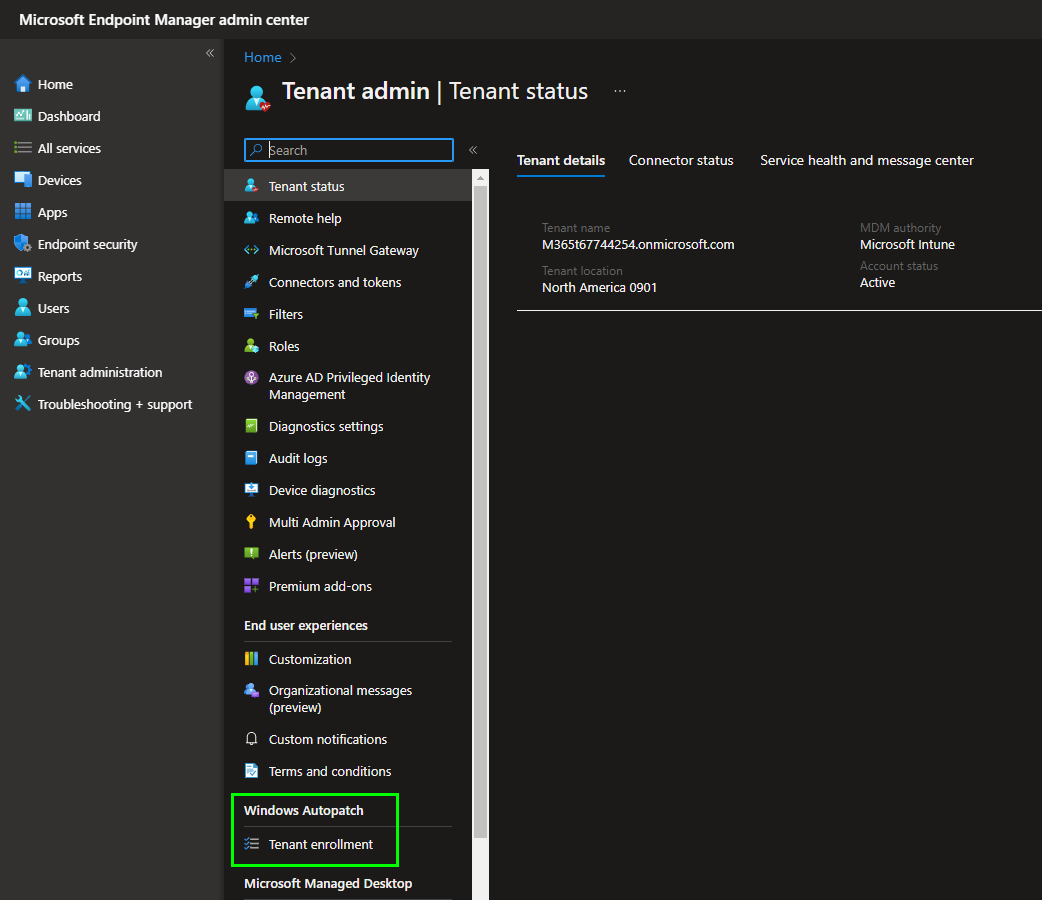
Here we have to agree to the terms:
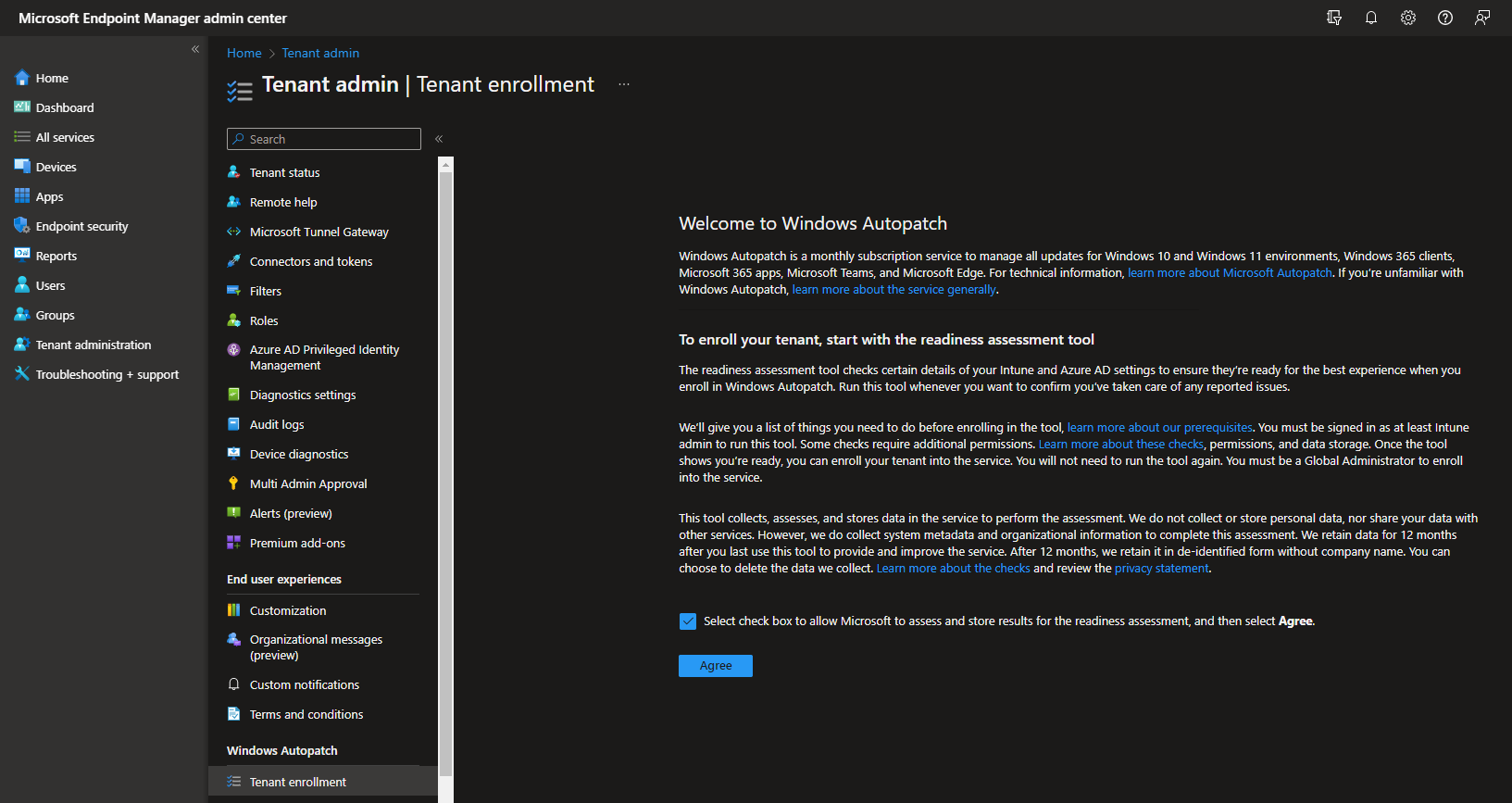
The service now checks whether all the requirements are met and reports the status „Ready“ if successful:
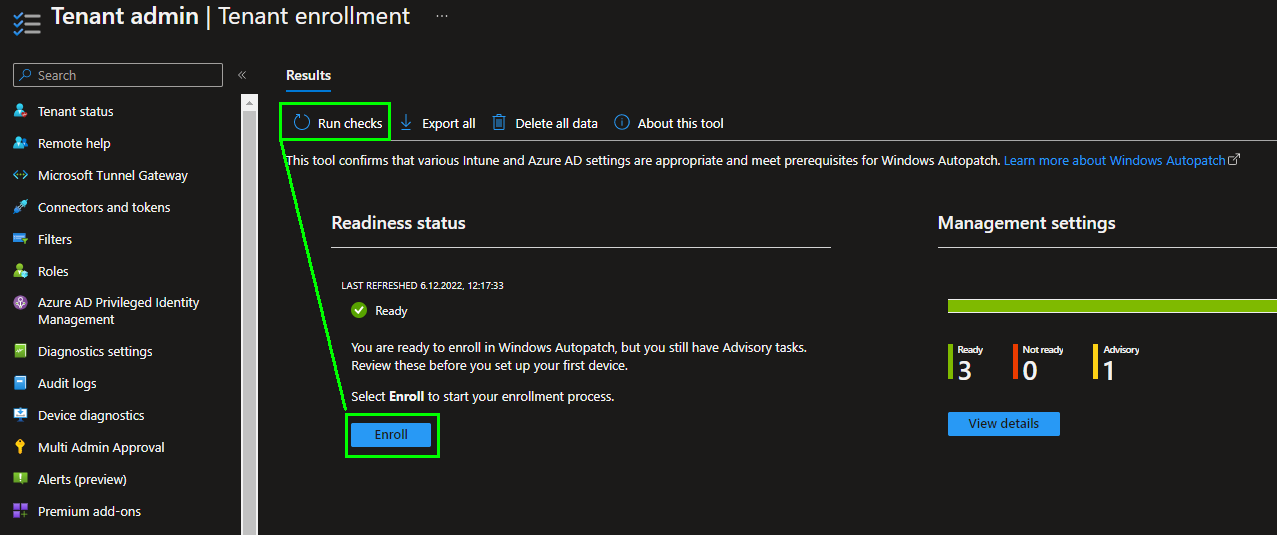
Readiness Status for Windows Autopatch
During the check, the readiness assessment tool reports one of the following 4 messages as a status:
- Ready: No problems, the enrollment can be carried out.
- Advisory: This message requires some steps to be configured. The individual steps are documented in the assessment tool.
- Not ready: There are basic requirements that are not met and must be configured first.
- Error: The Azure Active Directory roles that you have on the user used are not sufficient to carry out the enrollment.
Activate the Service
If the status is „Ready“, you can start the setup via „Enroll“. There you have to agree to the following conditions again:
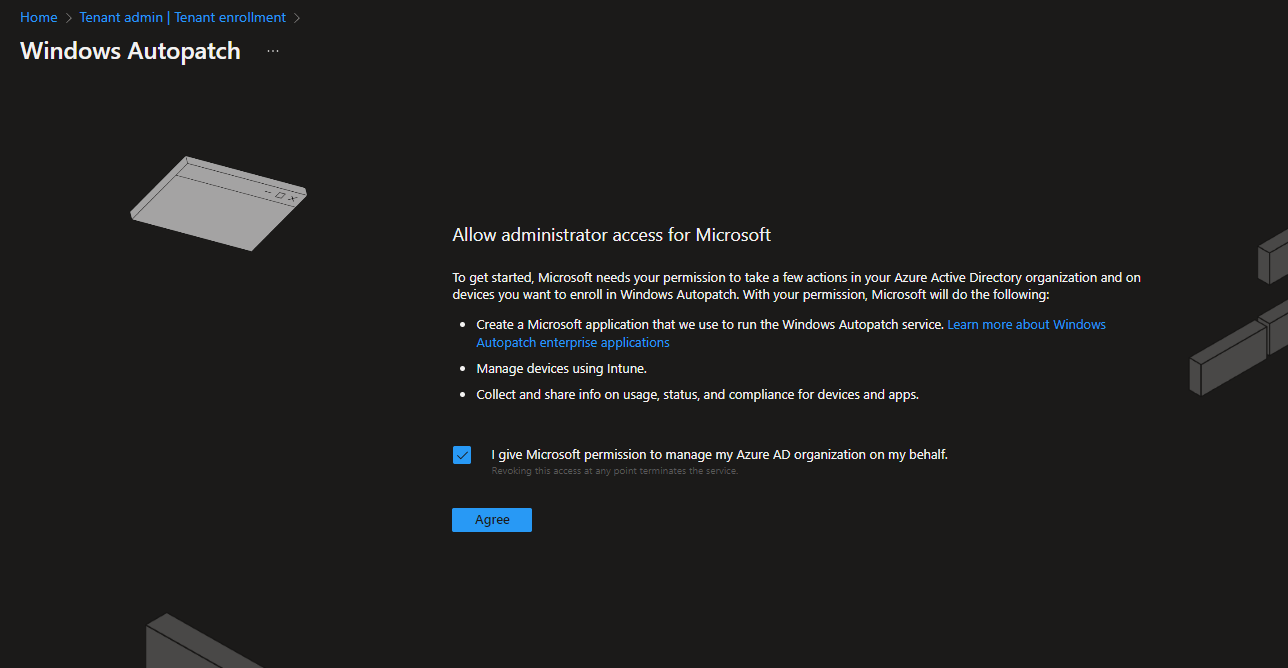
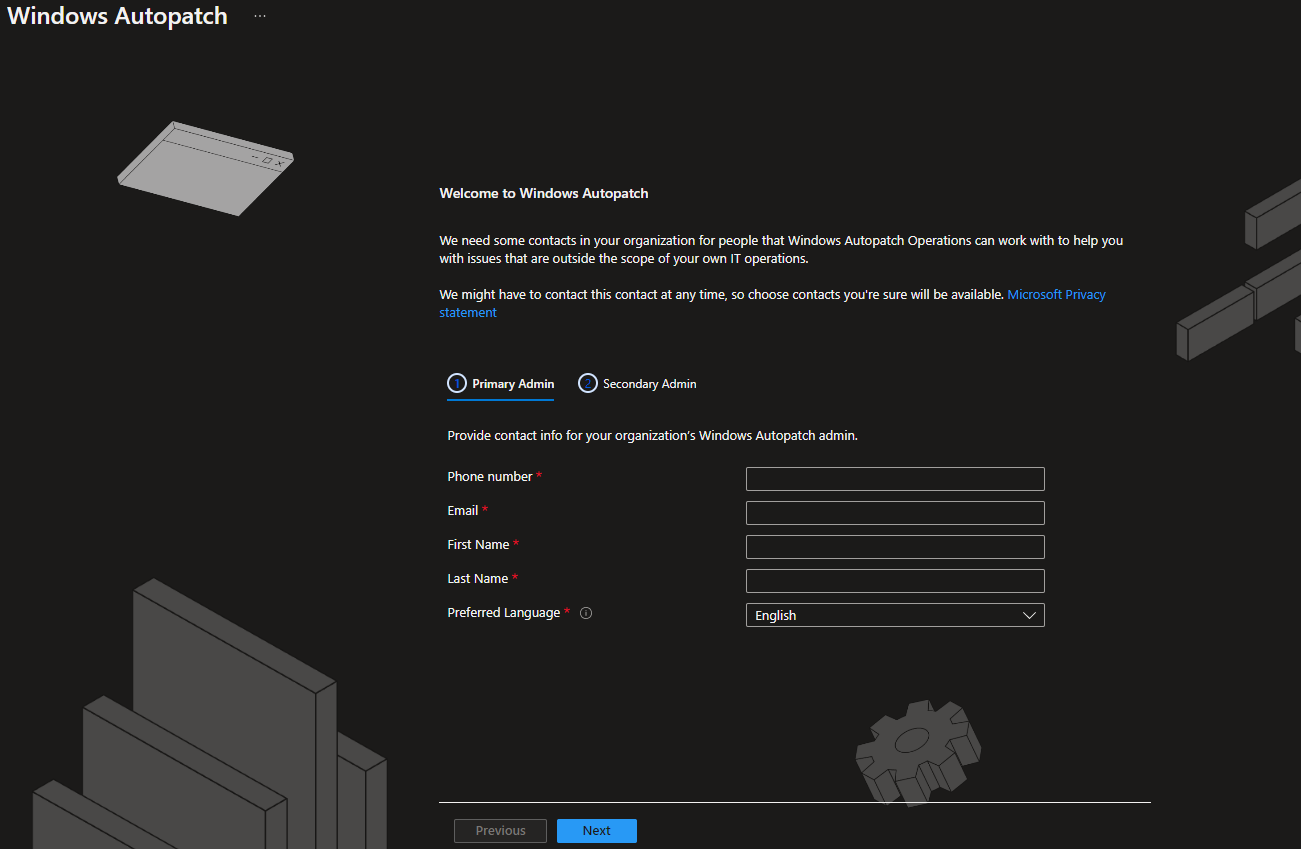
In addition, a contact person including a representative must be defined:
The service is now activated for the tenant:
The service is now set up and now we have to create some configurations so that the Autopatch Service can take over the patch management. To do this, we must first add the devices to the Azure AD group created by the service. A click on „Windows Autopatch Device Registration“ opens the group in Azure AD directly:
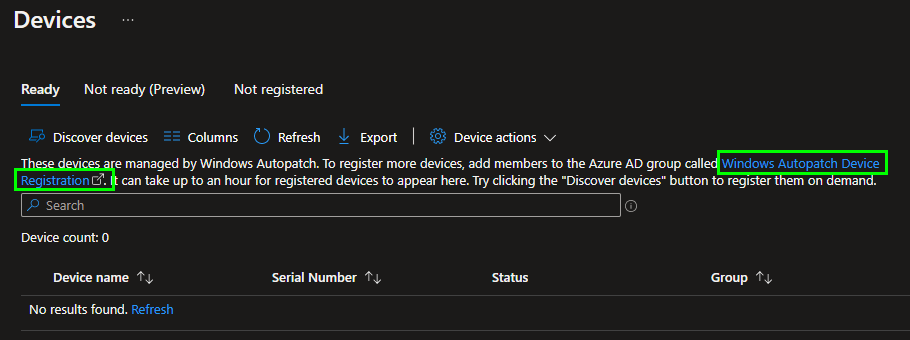
In the group we then add the computer accounts:
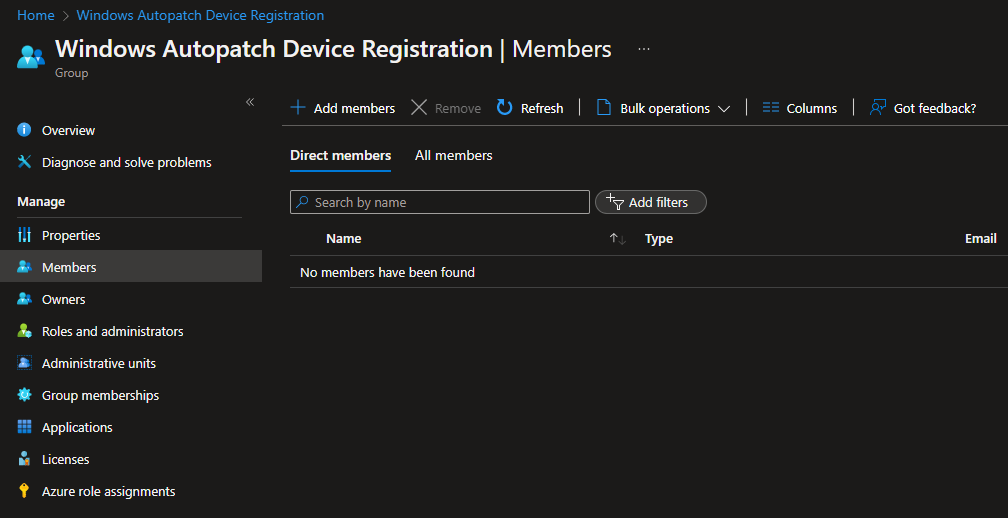
After adding the devices to this group, we need to search for devices in Intune in the Windows Autopatch Service:
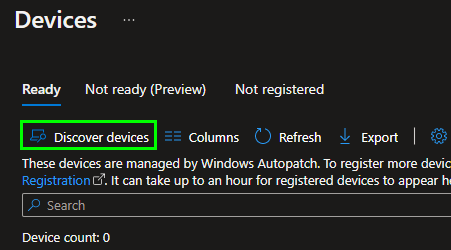
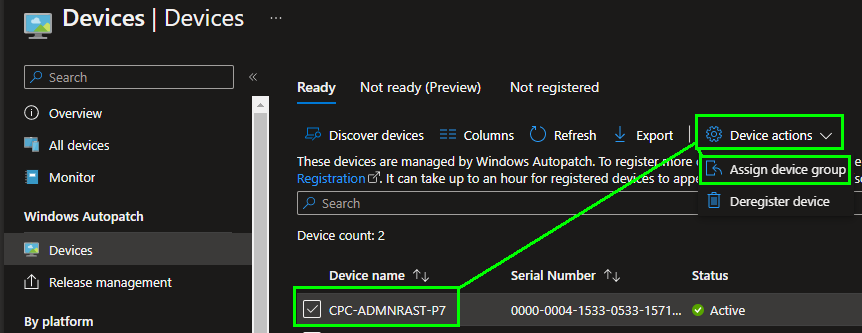
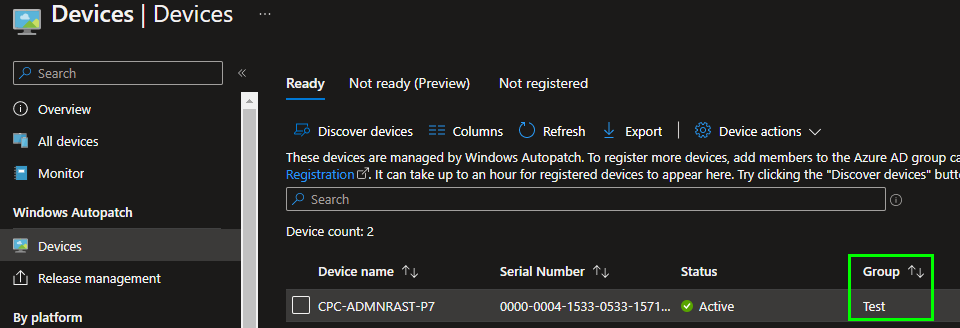
It may take up to an hour for the devices to show up here. Once the devices have appeared, you can add them to a distribution group:
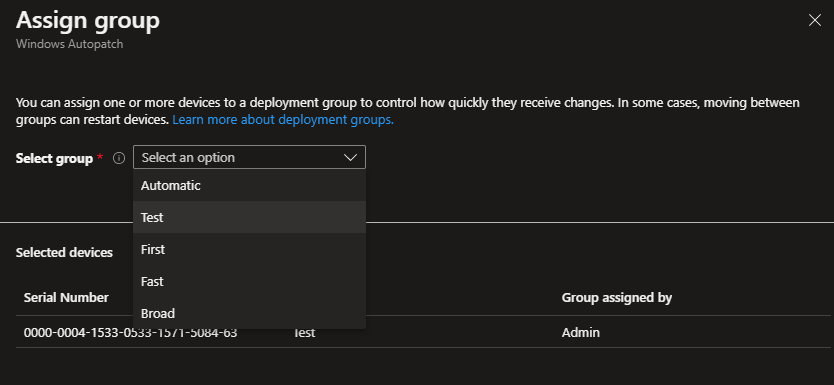
- Automatic: Intune automatically creates an assignment on one of the 4 groups.
- Test: This group should be chosen for pilot clients.
- First: This group should be chosen for the first distribution wave.
- Fast: This group should be selected for non-critical clients that can accept downtime.
- Broad: This group can be used for the large mass of devices.
After the assignment, the corresponding group is next to the device:
Rause or Rollback
The autopatch service makes it possible to pause or stop the rollout of updates and even roll them back later. The „Release Management“ can be used for this after the release of updates.
Azure AD Groups
The service creates the following groups in the Azure AD tenant:
| Groupname | Description |
|---|---|
| Modern Workplace-All | All Modern Workplace Users |
| Modern Workplace – Windows 11 Pre-Release | Test Devices Windows 11 Pre-Releases |
| Modern Workplace Devices-All | All Modern Workplace Devices |
| Modern Workplace Devices-Windows Autopatch-Test | Pilot Devices |
| Modern Workplace Devices-Windows Autopatch-First | Early Adopter Devices |
| Modern Workplace Devices-Windows Autopatch-Fast | Fast Rollout |
| Modern Workplace Devices-Windows Autopatch-Broad | All Devices for the broad rollout |
| Modern Workplace Devices Dynamic – Windows 10 | Devices with Windows 10 |
| Modern Workplace Devices Dynamic – Windows 11 | Devices with Windows 11 |
| Modern Workplace Roles – Service Administrator | All Users from the „Modern Workplace Service Administrator” Role |
| Modern Workplace Roles – Service Reader | All Users in Role “Modern Workplace Service Reader Role“ |
| Modern Workplace Service – Intune Admin All | All Users in Role “Intune Administrator“ |
| Modern Workplace Service – Intune Reader All | All Users in Role “Intune Reader“ |
| Modern Workplace Service – Intune Reader MMD | All Users in Role “Intune Reader MMD“ |
| Modern Workplace Service Accounts | Group for Service Accounts |
| Windows Autopatch Device Registration | Group for automatic Windows Autopatch Device registration |